Twitter: @armonio_liang , AC capital
Abstract:
In this article, we present two interconnected narratives: the first sketches the technical evolution of DeFi liquidity, while the second emphasizes the transformative impact of on-chain barter from an economic history perspective. Collectively, we aim to substantiate that a profound DeFi revolution is on the horizon, necessitating just a bit more patience. Those visionary builders who stay the course will eventually be rewarded by the market.
We meticulously trace the development of the decentralized exchange (DEX) market to illustrate that the emergence of on-chain barter, a true game changer, is far from a mere happenstance. It represents a significant chapter in the annals of Web3 builders’ history. Achieving its functionality has necessitated numerous innovations and improvements, not only within DEX but also across the underlying infrastructure layer.
Should on-chain barter ascend to the status of a key historical milestone, we assert that all related endeavors and contributions should be duly commemorated.
Do we lose control of our crypto?
Since January 2023, Bitcoin has reached its low point and rebounded to new highs, buoyed by ETF approval and new quantitative easing expectations. However, the prices of most altcoins have lagged behind. Some investors mock genuine innovations, dismissing the crypto world as a criminal domain. At various conferences, industry insiders have even labeled the entire sector as akin to a casino. Many crypto enthusiasts revel in the PvP (player versus player) excitement. While memecoins gain early popularity, valuable tokens are often overlooked.
Veteran players sense that this time is indeed different. Some builders are puzzled, questioning whether crypto can genuinely transform the real world. Since last year, many have shifted their focus to AI, while many more remain hesitant.
Why is the Crypto Market Different This Time?
We cannot ignore the impact of venture capital and team greed, misaligned interests, unethical behavior, and short-term thinking. The market is in a dark forest. Except for code, there are not too many rules to regulate participants. However, we propose an additional reason: the self-inflation within the crypto market is no longer sufficient to provide the necessary liquidity for our crypto ecosystem.
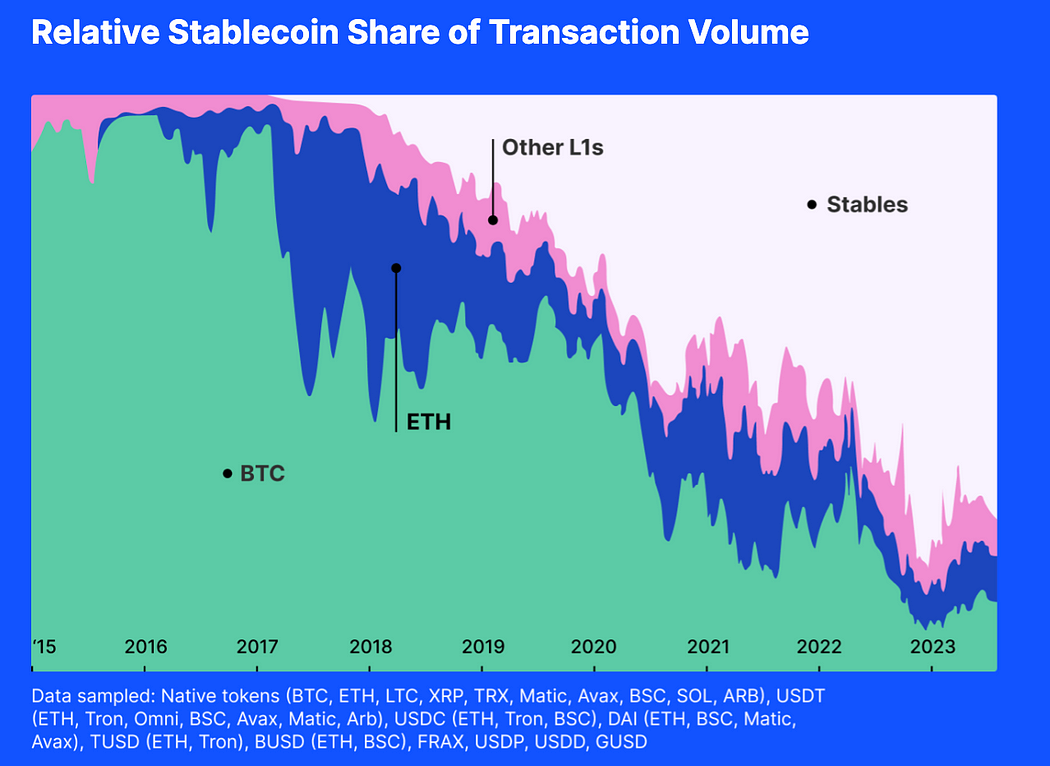
(resource:https://www.fixing.finance/report/the-future-of-stablecoin-design)
If we consider the share of the transaction volume, we can find the majority of the transactions was taken place by the USD stablecoin. If USD stablecoin market cap can not expand, the liquidity pool will be drained when new tokens are been issued continuously.
In history, since tokens can be others’ liquidity when Bitcoin and Ethereum are in a bull market, Altcoins seldom lack liquidity. But now, most of the trade pairs are composed of USD-pegged stablecoin. Bitcoin or Ethereum value’s explosions make it hard to inject liquidities into other tokens.
Crypto pricing power falls to Wall Street
All USD-pegged stablecoin and other compliance financial instruments are baits. Crypto follows a wall-street clock.
October, 2014, Tether started to provide a stable digital currency that could bridge the gap between cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies, offering the stability of traditional money with the flexibility of digital currencies. Now it has already become №3 Mcap token. Also, USDT has the maximum number of trading pairs in dex, 10 times more than Ethereum or wBTC.
In September 2018, USD Coin (USDC) is launched by Circle, in collaboration with Coinbase, under the Centre Consortium. It is pegged to the US dollar, with each USDC token backed 1:1 by USD held in reserve. As an ERC-20 token, USDC enables seamless transactions and integration with various decentralized applications.
On December 10, 2017, The Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) was the first to launch Bitcoin futures. Even if only USD settled the future, it still could influence the spot price of Bitcoin, especially, now the open interest has reached 28% of the whole global market.
Not only physically, Wall Street also influences the crypto market psychologically. Do you still remember when we started to be concerned about the attitude of the Fed, the haircut of the trust from Greyscale, the “dot-plot” from FOMC, and the cashflow of BTC-ETF. All of those information impacts our behaviors psychologically
Stablecoin is the bait dropped by the US government. Since we accept USD-pegged stablecoin as a means to provide liquidity, it started accumulating its consensus, taking place the liquidity role of the crypto native token, competing and undermining the credit of other tokens. USD gradually became dominant in the universal equivalent market.
In this way, we are losing our market rhythm.
I don’t mean to blame USD-pegged stablecoin, conversely, it is a natural result of fair competition and market choice. Tether and Circle help investors invest crypto with USD-pegged assets directly onchain, expose them to USD-equivalent risk onchain, and give investors more options.
We are all struggling for liquidity!
Attack on DeFi: technology is our wings
Liquidity is Always the Real Demand
Liquidity is a fundamental characteristic of a market. Any innovation that improves market liquidity marks a significant historical advance.
According to organization theory, a market is defined as a structured environment where exchanges of goods, services, and information occur between buyers and sellers. This environment is guided by established rules, norms, and institutions that facilitate coordination, reduce transaction costs, and support efficient economic interactions.
Liquidity is crucial for a market organization as it directly influences the efficiency, stability, and attractiveness of the market. High liquidity reduces transaction costs by minimizing slippage and increasing transaction volume. A market with high liquidity also exhibits greater price resilience, helping to find more accurate price information. Information economics emphasizes a market’s role in information discovery. In an ideal market, information flows freely, enabling participants to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and achieve equilibrium prices. A high-liquidity market generates robust information, aiding in more efficient resource distribution.
Whether it is price discovery efficiency, price stability and resilience, or low trade costs, all these characteristics enhance a market’s ability to attract participants. Therefore, it is essential for any market to increase its liquidity.
Money is an innovation to relieve the liquidity problem.
Academically, there are two prevailing theories about the origin of money. One considers money as a convenient means for trading, which is adopted by the masses and scholars. The other comes from the book “Debt: The First 5000 Years” by David Graeber. He believed that money was derived from debt relationships, but he also admitted money’s universal equivalent role.
In addition to “A History of Money: From Ancient Times to Present Day” by Glyn Davies and “Capital: Volume One” by Karl Marx, there are other resources that hold similar opinions on the origin and evolution of money.
For instance, in “The Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the World” by Niall Ferguson, the author argues that the development of money also originated from the need for an efficient system of exchange in societies, which started with barter and evolved to a more complex system using objects with intrinsic value.
Similarly, in “Money: The Unauthorized Biography” by Felix Martin, the author also touches on the concept of money as a social technology, developed from a need for a more efficient system of exchange. Martin, like Marx, identifies money as a universal equivalent that emerged from a common commodity in the barter era.
Lastly, “Debt: The First 5000 Years” by David Graeber offers a unique perspective, proposing that money evolved from systems of debt and obligation that predated the invention of money itself. However, Graeber’s view still aligns with the central idea that money was created as a universal equivalent to facilitate the exchange of goods and services.
These resources further emphasize the role of money as a medium of exchange echoing the viewpoints of both Davies and Marx.
In conclusion, money is the ancient elites answer to the market liquidity problem before the value Internet network. Money is the means of increasing liquidity.
Old forces used to equal money to liquidity seldom tried to improve the organizational structure of the market to achieve a better liquidity situation, they never considered market liquidity without money. Maybe that is because they are like fleas trapped in a box with lids too long to forget how high they can jump.
Endeavors by DEX
The primary goal of any market is to provide the most accurate price and the most efficient resource allocation. Every component, mechanism, and structure is designed to achieve this purpose. Since ancient times, humans have continuously created new methods to enhance market efficiency.
Over the centuries, markets have evolved significantly. The mechanisms for price generation have undergone multiple upgrades. Various settlement procedures, such as dealer markets, order-driven markets, brokered markets, and dark pool markets, have been developed to meet different economic demands.
Blockchain Came: A New Play
With the advent of blockchain technology, we encountered new constraints and feasible solutions to the old liquidity game. We had to create innovative methods to settle swap demands and provide liquidity to tokens. Token exchanges face a trilemma: 1) sufficient liquidity, 2) efficient pricing, and 3) decentralization.
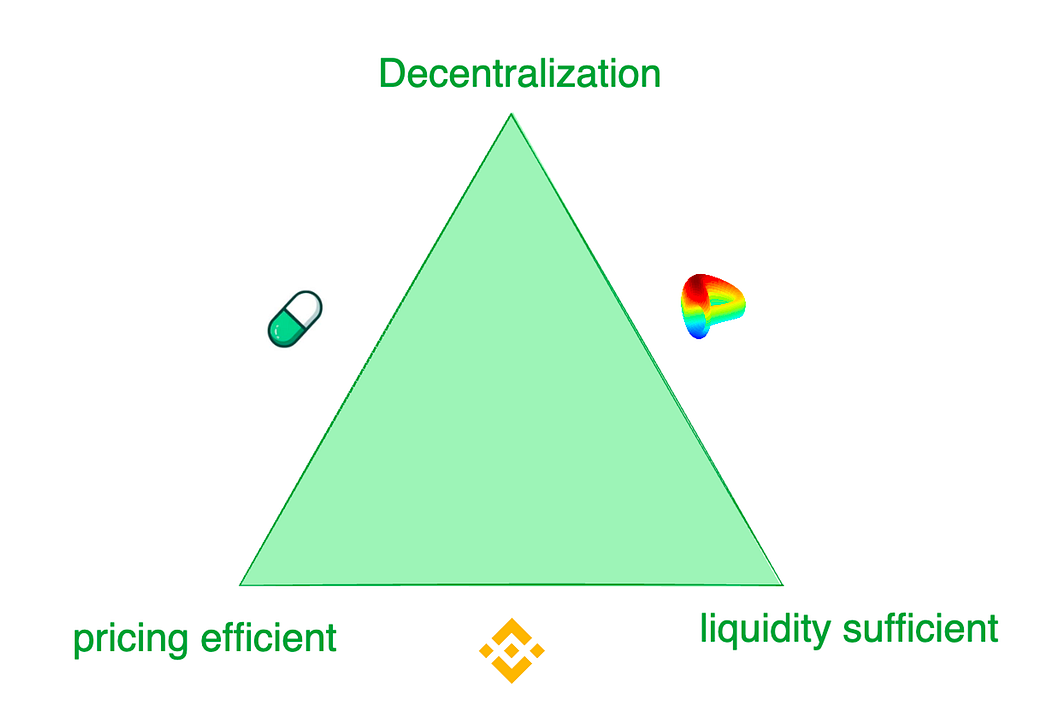
Trilemma of exchanges
While centralized exchanges like Binance offer the best trading experiences, they are plagued by risks such as fraud and monopoly. In contrast, decentralized exchanges cater to different demand scenarios. For instance, Pump.fun provides extremely sensitive token supply curves, while Curve offers the best liquidity for most situations rather than price-discovery sensitivity. These exchanges employ various patterns to meet the trading preferences of their diverse target customers.
Decentralized exchanges have made significant strides in addressing this trilemma and other on-chain trade challenges through innovative solutions. Uniswap serves as a benchmark in this sub-industry. The innovation of the bonding curve marked the beginning of a new era. Before Uniswap’s “X*Y=C” curve, decentralized exchanges used order books to settle on-chain trading demands. Subsequent Automated Market Makers (AMMs) followed Uniswap’s discovery direction by creating liquidity pools. In Uniswap V2, liquidity in different trading-pair pools was connected by algorithms. Uniswap V3 introduced segmentation liquidity pools, allowing users to define the price regions they want to provide liquidity for. Uniswap V4 further advanced this by offering a liquidity-pool-customization solution.
Curve Protocol, focusing on stable-coin transactions, developed its own supply liquidity curve to provide more token liquidity around a predetermined equilibrium point. To address the challenge of joint liquidity pools, Curve Protocol invented a multi-dimensional formula, enabling users to place more than two tokens in a single liquidity pool, thereby sharing liquidity among all tokens in the pool. In practice, centralized exchanges (CEXs) demonstrate better liquidity and pricing efficiency. On-chain pricing systems often lag behind off-chain CEXs. Hashflow established Professional Market Maker Pools (PMMs) with the help of oracles to connect on-chain and off-chain liquidity.
However, for small-scale tokens, traditional bonding curves are expensive. Friend.tech designed a steeper bonding curve to accommodate smaller investors who prefer price surges over sufficient liquidity. As token value scales increase, investor preferences shift towards liquidity. Inspired by this, Pump.fun uses a steep curve when token value is low but transitions to a different slope or even a different curve as the value increases.
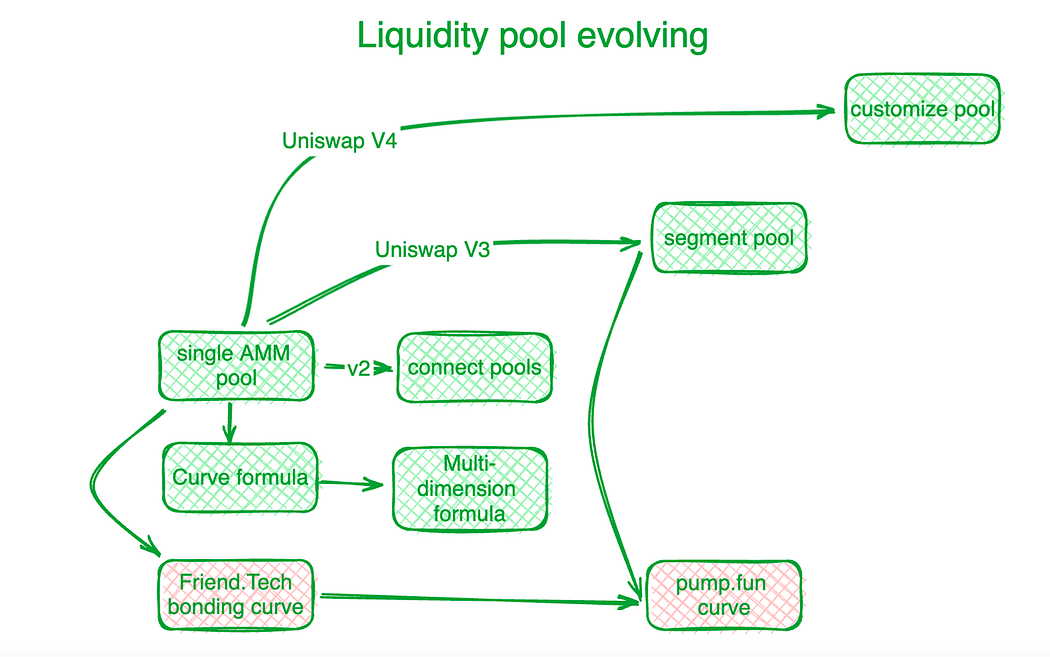
Liquidity pool evolving
MEV, a special liquidity competition onchain
Maximum Extractable Value (MEV) refers to the profit a miner or validator can make through their ability to arbitrarily include, exclude, or reorder transactions within the blocks they produce. It can be regarded as a liquidity cost. In a liquidity pool, every exchangeable token (liquidity) is distributed along a price scale, and the liquidity at each price span is limited. Those who can interact with the liquidity pool contract earlier gain an advantage by securing better prices. In this way, MEV is inherently tied to the liquidity problem.
MEV manifests in decentralized transactions through the acquisition of favorable liquidity by sorting transactions. This competition enhances the efficiency of on-chain transactions but also harms the interests of various parties involved. To retain as much transaction value as possible within decentralized exchanges and return it more completely to participants, developers build algorithms and mechanisms at the application level to intercept MEV generated by transactions.
As a veteran in MEV management, Flashbots focuses on the distribution of node benefits. To ensure transparent and efficient MEV distribution, they have established an MEV auction system at the node level. The Eden Network pursues similar objectives. KeeperDAO integrates MEV extraction and staking cooperatively, allowing participants to benefit from MEV while protecting users from its adverse effects. Jito Labs, a liquidity staking project on the Solana network, also addresses this issue.
Projects led by Cow Protocol, including UniswapX and 1inch Protocol Fusion, use auction interaction rights to retain MEV within the transaction process rather than allowing it to migrate to the node accounting level. Intercepting MEV protects active traders and the AMM liquidity pool, eliminating the previous dilemma of DEX bribing nodes and MEV loss.
Scattered Liquidity Calls for Agents to Solve the Problem
As previously mentioned, token liquidity is fragmented across various customized pools controlled by different protocols on different blockchains or layer 2 solutions. Polygon proposes an aggregate layer concept to collect liquidity from different layers. Initially, some decentralized exchange (DEX) aggregators emerged to consolidate liquidity from these disparate pools. However, after accumulating sufficient traffic, a more efficient approach was to create platforms that foster competition, such as 1inch and Cow Protocol.
Furthermore, the batch auction mechanism enhances the role of agents. It introduces a new market mechanism to alleviate liquidity constraints. In practice, traders are allowed to place orders at limited prices within a specified period. The batch-auction smart contract collects these orders and bundles them into a batch. The smart contract then permits agents to bid on these batches. The agent who offers the best price wins the opportunity to settle all the potential transactions within the batch.
An illustration of the batch auction mechanism on CoW Protocol
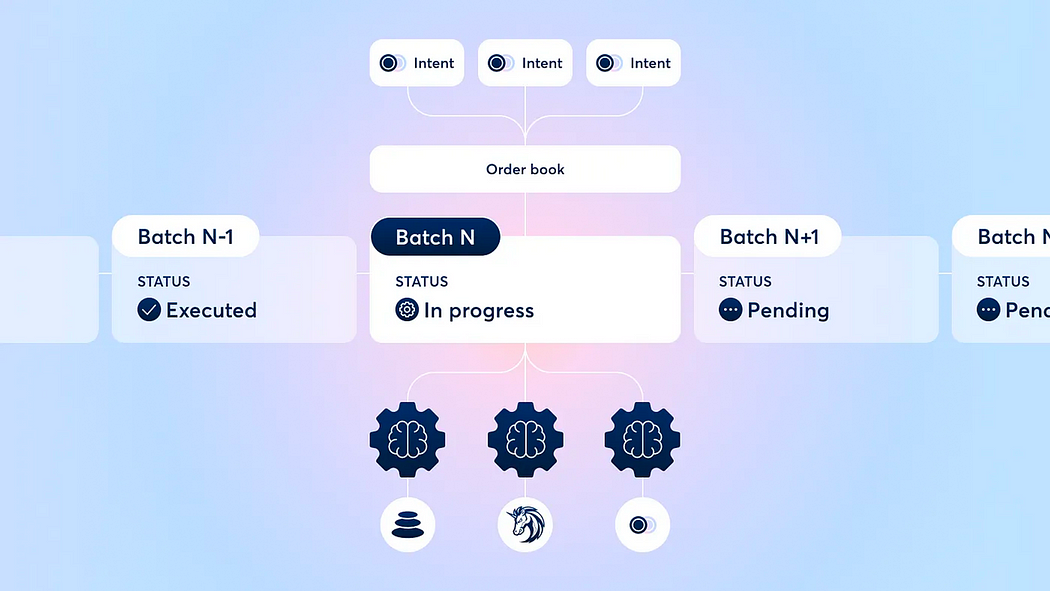
Batch auction draft from Cow Protocol
Batch auction: The epitome of DeFi development
After years of DEX development, the industry accepts methods like batching, auctioning, and matching of orders to optimize trading outcomes for all participants. Specific implementations of the auction mechanism differ, but generally, they shift the complexities of optimizing swap outcomes to specialized participants and redistribute the surplus back to relatively unsophisticated swappers.
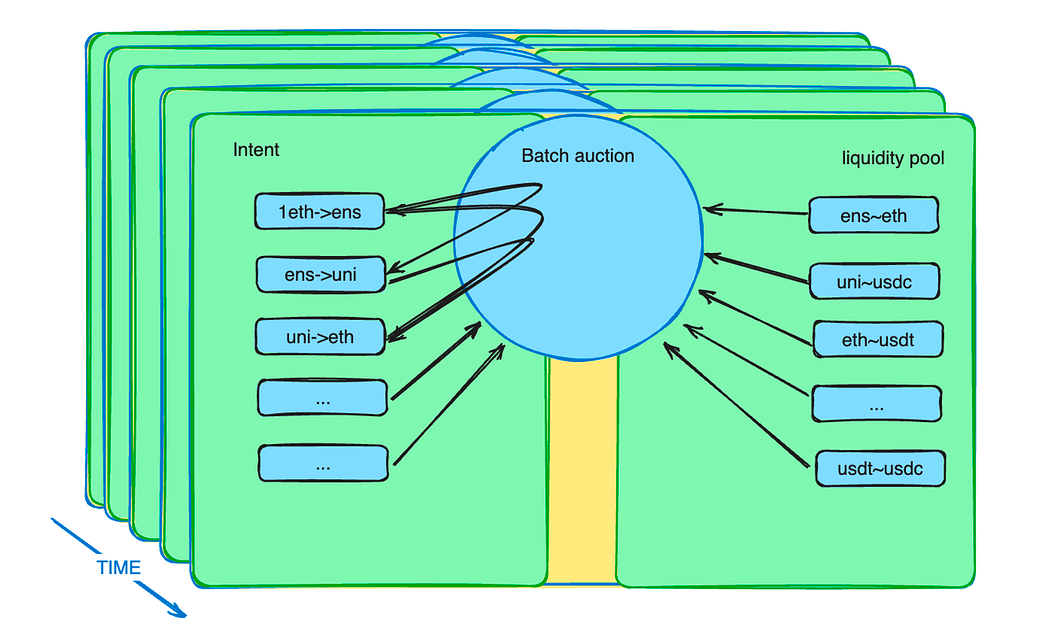
Batch auction schematic diagram
This kind of auctions can solve many DEX dilemmas in more than one aspect.
Despite the MEV redistribution mentioned in the previous sector, batch auctions can do much more. What the trader sends to the smart contract is not instruction but an intent. The intent can last for several minutes. These intents bundle into a batch and propose to a group of specific trading agents competing with each other. As we know, there are tons of intents and various liquidity pools, optimization is a difficult problem. Professional matters are handed over to professionals, which improves system efficiency.
By sacrificing time efficiency( every trade intent default lasts for minutes), batch auction tried to maximize its value efficiency, forming differentiated competition with CEX.
What is more? Barter resurgence!!
Barter Returns to the Market
As the ancestor of all cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin defines itself as a currency. The decentralized market is a new, emerging landscape with no explicit consensus constraints. Barter, a crypto-native trade pattern, fits naturally into this environment.
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are often referred to as “swap” platforms. In their trade model, there is no pre-determined universal equivalent role. Traders are not forced to use fiat money or stablecoins as intermediaries. At the liquidity pool level, any trading pairs are allowed. Traders can use any tokens they prefer to exchange for other tokens, enduring liquidity inefficiency costs.
However, relying solely on liquidity pools for barter trading has significant limitations. There are not enough pairs for all types of barter trades. Due to the structure of liquidity pools, liquidity is deployed over a long time, making it difficult to find the equilibrium price. Therefore, liquidity must be deployed in a broader price range, leading to scarcity compared to the limited-time demand of intents. This is where intents and batch auctions come into play.
Suppose there are several potential trade intents that can meet each other’s demands, supplemented by liquidity from pools. In that case, barter will return to the market in a more efficient state. As the scalability of web3 infrastructure improves and more bulk commodities and financial instruments onboard to web3, batch auction smart contracts will capture thousands or even millions of trade intents every second. Any token can then act as a means of liquidating other tokens. We will be free from the liquidity constraints imposed by the USD in a universal context.
Batch Auction: The Key to On-Chain Barter
The resurgence of barter represents a renaissance, echoing the demands of the market.
Historically, when money was invented, traders struggled to find direct barter opportunities that met their immediate needs. As a result, they exchanged goods for a universal equivalent (money) to later purchase what they truly needed in another transaction. This exchange pattern, once widely accepted, forced real barter demands to split into at least two steps. Consequently, direct barter markets vanished.
Today, on-chain barter demands exist as intents for short periods. Batch auction smart contracts collect these intents. Anyone, whether a human or an AI agent, who offers the most favorable bid can fulfill the entire batch of transaction demands. If the intents match, there is no need for USD-pegged stablecoins. Tokens retain their utility, sharing liquidity as before.
In the short term, the presence of intent timespans allows arbitragers to move liquidity across chains and from off-chain to on-chain. For example, an algorithm that spots a price gap between different chains or between DEX and CEX can buy at the lower price and sell at the higher price within the allotted time. It may need to hedge market risk using financial instruments to achieve a risk-free condition. However, in the future, when on-chain, off-chain, and cross-chain transactions can be synchronized, all transactions could be executed simultaneously. This could eliminate risk costs, providing the best experience for traders.
Why is Barter a Milestone?
The reason is straightforward. If we look back at the history of money, the right to mint coins was originally private. According to “Debt: The First 5000 Years,” debt could be personal. Even in modern times, as detailed in “A Monetary History of the United States, 1867–1960,” private individuals could mint silver coins. Today, however, all credit is issued by the US Federal Reserve. Even Bitcoin is measured in USD, which is unfortunate. The USD has overshadowed crypto, but barter offers a chance to reclaim that prominence.
The development of decentralized exchanges (DEX) gives us confidence that we can eventually surpass centralized exchanges (CEX). During the last DeFi summer, there was a widespread belief that DEX would overtake CEX in due time. How many still hold that belief today? If we examine the evolution of DEX, the introduction of batch auctions is not coincidental. It is a deliberate step toward solving liquidity issues. DEX has evolved from merely having liquidity pools to becoming a comprehensive liquidity system, with different participant roles, specialized components, and permissionless composability. This progress has been achieved through the efforts of predecessors.
One business cycle has passed, and although the giants in DeFi remain unchanged externally, they have transformed internally. Batch auctions represent a significant milestone, as important as the invention of liquidity pools. I believe they can fulfill the dream of DEX surpassing CEX. When barter becomes the main trading pattern again, we can regain control of our market rhythm.
Postscript:
In my discussions with numerous industry professionals about the future, I found a pervasive sense of confusion. The market’s failure to value technology has led to a widespread lack of confidence. I vividly recall a conversation at the end of 2018, early 2019, over a hot pot in Chengdu with a friend. He spoke passionately about DeFi and the promising future of Ethereum, his eyes shining with excitement despite ETH’s price being below 90 USD at the time.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) represent just a small segment within the expansive DeFi industry. When we take a closer look, we can discover significant and exciting progress happening across various DeFi tracks. As long as technology continues to advance and evolve, rather than stagnate, what do we have to worry about? Dreams will eventually come true.
To all the builders in the industry, I offer a Chinese poem for encouragement: “Don’t worry about having no friends on the road ahead; who in the world doesn’t know you. (莫愁前路无知己,天下谁人不识君。)”
Thanks to @Jialin’s help, with the encouragement from NewMingshiS, Observer completed the last observation record at Amed Beach trip in Bali this time
Reference:
Debt: The First 5000 Years
Money: The Unauthorized Biography
The Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the World
A History of Money: From Ancient Times to Present Day
Das kapital
The Future of Stablecoin Design
https://www.fixing.finance/report/the-future-of-stablecoin-design
Uniswap Labs and Across Propose Standard for Cross-chain Intents
https://blog.uniswap.org/uniswap-labs-and-across-propose-standard-for-cross-chain-intents
Understanding Batch Auctions
https://blog.cow.fi/understanding-batch-auctions-89f0f85e6c49#:~:text=A batch auction is a,rules that prevent MEV attacks.
Uniswap v2 Overview
https://blog.uniswap.org/uniswap-v2
Introducing Uniswap v3
https://blog.uniswap.org/uniswap-v3
Aggregated Blockchains: A New Thesis
https://polygon.technology/blog/aggregated-blockchains-a-new-thesis
A deep dive into 1inch Fusion
https://blog.1inch.io/a-deep-dive-into-1inch-fusion/
Priority Is All You Need
https://www.paradigm.xyz/2024/06/priority-is-all-you-need
Quantifying Price Improvement in Order Flow Auctions
https://blog.uniswap.org/UniswapX_PI.pdf














